
- SOPRANO AUDIO
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- MEZZO SOPRANO
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- ALTO VOICE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- COUNTER TENOR
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- TENOR VOICE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- BASS VOICE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.






- PICCOLO
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- FLUTE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- OBOE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- COR ANGLAIS
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- CLARINET
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- BASS CLARINET
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- SAXOPHONE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- BASSOON
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- DOUBLE BASSOON
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.

Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- HARP
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- VIOLIN
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- VIOLA
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- CELLO
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.

- TRUMPET
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- FRENCH HORN
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- TROMBONE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- TUBA
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.



- TIMPANI
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- XYLOPHONE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- GLOCKENSPIEL
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- TUBULAR BELLS
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.

- GONG
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- SNARE DRUM
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- BASS DRUM
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- TRIANGLE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- WOOD BLOCK
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- TAMBOURINE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.

- ACCORDION
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- FIDDLE
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- ACOUSTIC GUITAR
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- BAGPIPES
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- CLARSACH
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- BODHRAN
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.


- GUIRO
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- CASTANETS
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- BONGO DRUMS
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- SITAR
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- TABLA
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- STEEL DRUM
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- PAN PIPES
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.


- PIANO
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- HARPSICHORD
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- ORGAN
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- KEYBOARD
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- SYNTHESIZER
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.






|
B flat major and G minor |
|
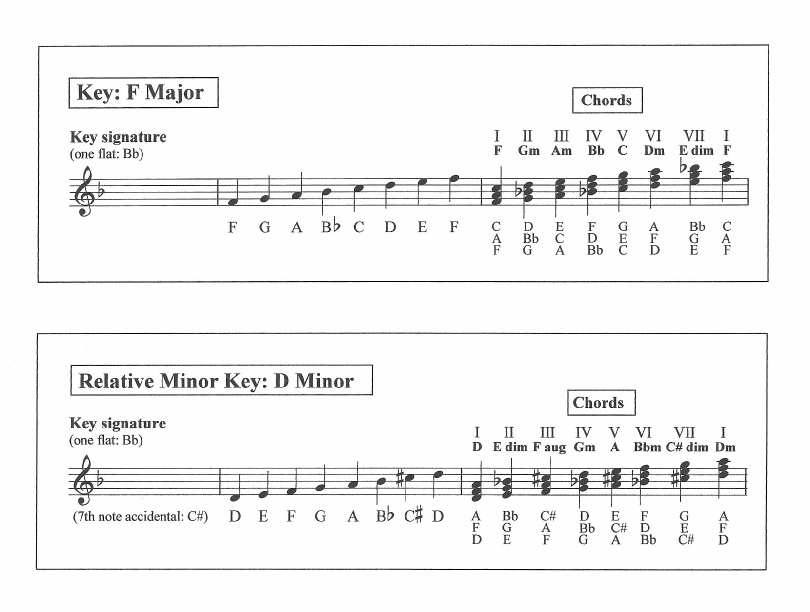
F major and D minor |
|
E major and C sharp minor |
|
A major and F sharp minor |
|
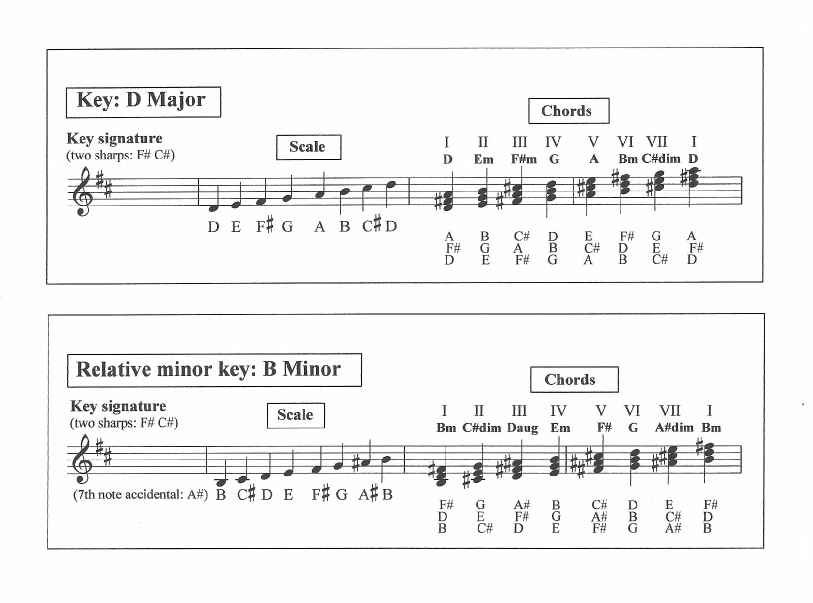
D major and B minor |
|
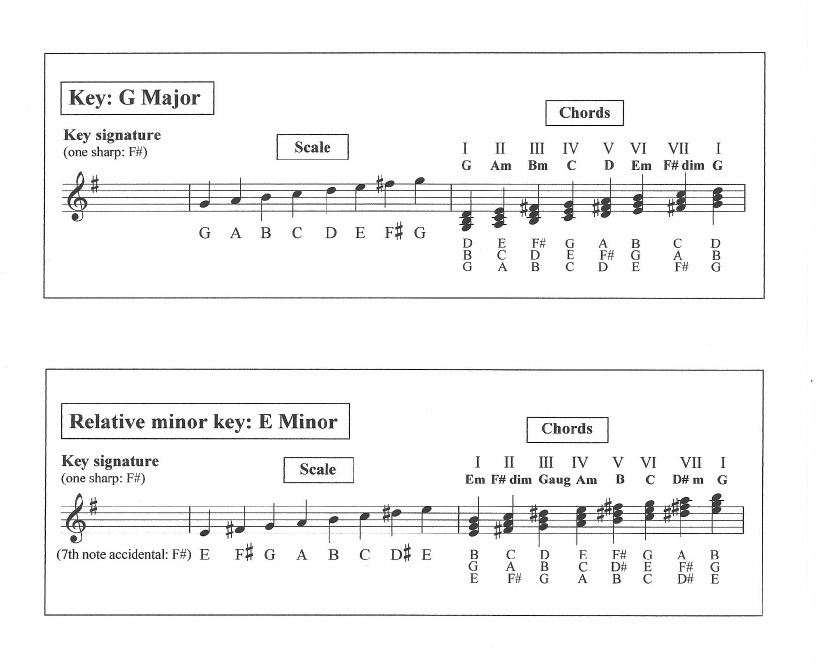
G major and E minor |
|
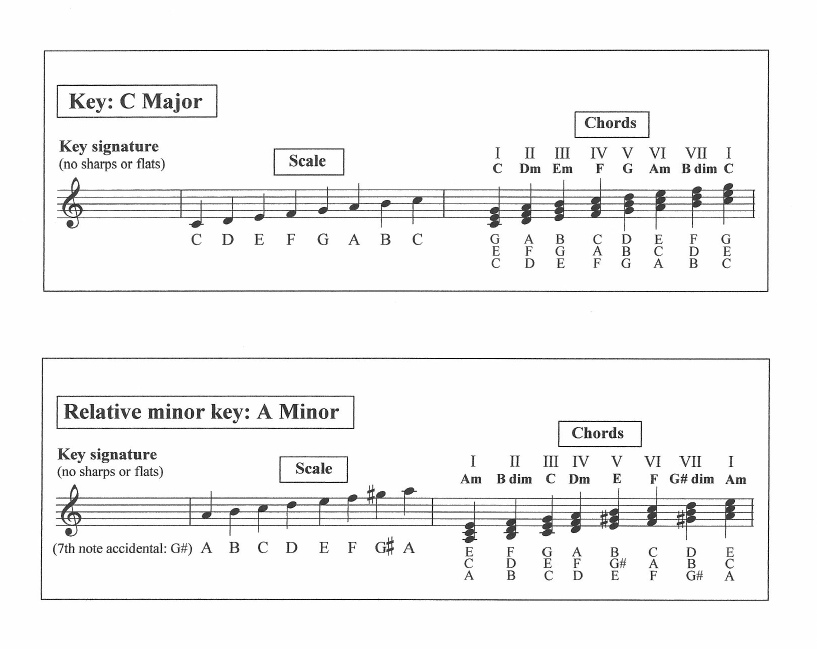
C major and A minor |


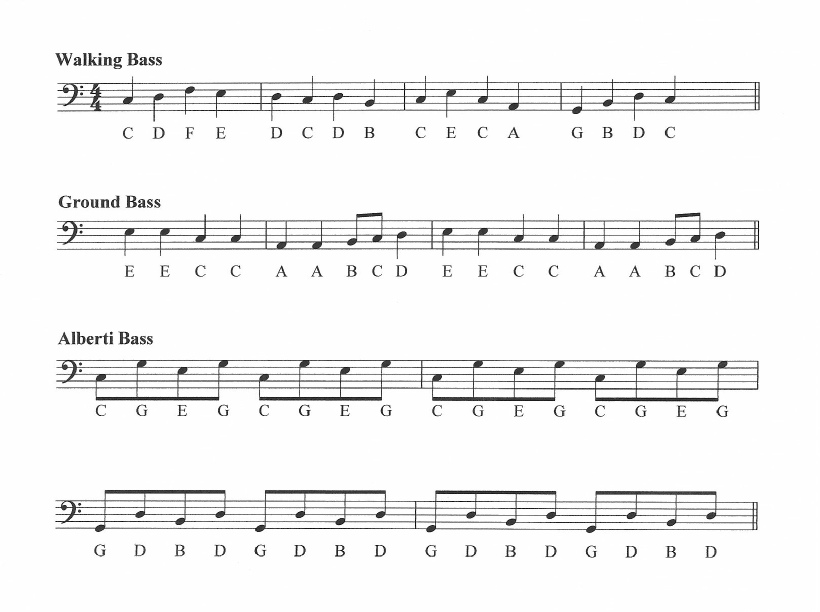
- Walking Bass
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- Walking Bass 2
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- Alberti Bass
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- Ground Bass
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- 6/8 time
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- 9/8 time
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.
- 12/8 time
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.